Poisonings vs. Adverse Reactions vs. Toxic Effects vs. Underdosing Definition
Poisoning: reaction to the improper use of a medication. This can include either:
Wrong substance
Wrong dose
Wrong person
Wrong Route of administration
Taken in combination of alcohol, illicit medication, or with over-the-counter medications that have not been approved by a provider.
Adverse Reaction: reaction when a substance is taken correctly as directed.
Toxic Effect: reaction or effect due to the exposure to a substance that is not a medication.
Underdosing: taking less of a medication, than a provider or manufacture’s instruction.
Coding Considerations:
T36-T50 code groupings correlate to Poisoning, Adverse Effects & Underdoing. T51-T65 code groupings correlate to Toxic Effects
Sequencing Guidance:
Poisoning:
PDx will be poisoning code (T36-T50) with the manifestation(s) sequenced as a Secondary Diagnosis
Example:
Pt. presents with Acute Pulmonary edema due to accidental heroin overdose in a patient who is heroin dependent.
PDx: Poisoning by heroin, accidental (unintentional), initial encounter (T40.1X1A)
SDx: Acute pulmonary edema (J81.0) MCC
SDx: Opioid dependence (F11.20) CC
DRG: 917 Poisoning & toxic effects of drugs w MCC
Adverse Reaction:
PDx will be the manifestation, symptom, or adverse effect followed by the appropriate code for the adverse effect of the drug (T36-T50)
Example:
Pt. presents with Toxic Encephalopathy from Digoxin toxicity. Upon questioning the pt. admits to taking the medication as prescribed.
PDx: Toxic Encephalopathy (G92.9)
SDx: Adverse effect of cardiac-stimulant glycosides and drugs of similar action, initial encounter (T46.0X5A)
SDX: 093 Other disorders of Nervous System without CC/MCC
Toxic Effect:
PDx will be the toxic effect code (T51-T65) with the manifestation(s) sequenced as a Secondary Diagnosis
Example:
Pt. presented with suicide attempt, drinking Drano. Admitted for erosive esophagitis with bleeding and blood pressure monitoring.
PDx: Toxic effects of corrosive alkalis and alkali-like substance, intentional self-harm, initial encounter (T54.3X2A)
SDx: Ulcer of esophagus with bleeding (K22.11) MCC
DRG: 917 Poisoning and Toxic Effects of Drugs with MCC
Underdosing:
The PDx will be the manifestation, symptoms, or adverse effect, followed by the appropriate code for the adverse effect of the drug (T36-T50)
Example:
Pt. presented with HTN urgency after stopping all their antihypertensive medications on their own.
PDx: HTN Urgency (I160)
SDx: Underdosing of other antihypertensive drugs, initial encounter (T46.5X6A)
DRG: 305 Hypertension without MCC
Chronic conditions related to alcohol or drug abuse, or dependence are not classified as poisoning. The code for the chronic condition is sequenced first, followed by a code for the abuse or dependence. For example:
| K70.30 + F10.20 | Alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver; chronic alcohol dependence |
| K70.10 + F10.20 | Alcoholic hepatitis; chronic alcohol dependence, episodic |
| F14.14 | Drug-induced depressive state due to cocaine abuse |
CDI Practice Considerations
Since sequencing and thus DRG assignment is determined by the circumstance of the event, always make sure the adverse reaction, poisoning, toxic effect, or underdosing is clearly documented along with the medication or other toxic substance and query, as necessary.
Overdoses are considered poisoning.
Drug Toxicity due to a medication is either an adverse effect or poisoning, NOT a toxic effect. Query if the documentation is not clear.
Common Manifestations to review and potentially query for:
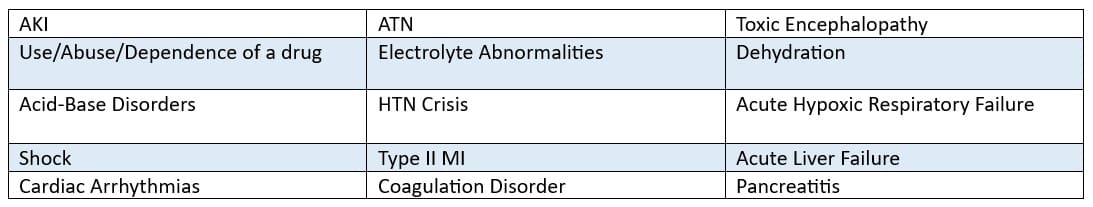
Be aware of the reason, if known, for the underdosing. If related to financial hardship, this could map to Z91.190 Patient’s noncompliance with other medical treatment and regimen due to financial hardship, or Z91.A20 Caregivers intentional underdosing due to financial hardship, supporting capture of Social Determinants of Health code. Refer to Official Coding Guideline I.C.21.c.17 ‘Social Determinants of Health’ for additional guidance.
Looking for CDI help?
Learn more about e4health CDI Solutions. Our Team is leading the way in the CDI industry.
e4health CDI Education
Need help to earn CEUs or education your team? Visit the IQ Education Center and get your free account or contact us for more information.
e4health is dedicated to elevating the business of healthcare. We are committed to offering support and the most current information and updates to collaborate with coding and CDI professionals to realize their fullest potential. We enthusiastically seek opportunities to develop ourselves and each other. We understand that knowledge is the key to success for our clients navigating the ever-changing health information management landscape.

Earn FREE ACDIS CEUs when you join Staci Josten, RN, BSN, CCDS, Alyson Swinehart, BSN, RN, CCDS, and other CDI leaders for a roundtable discussion regarding important, timely industry topics! The topic for December’s discussion is: Clinical Validation. We will provide background on this topic, share industry insights, and facilitate collaborative discussion with guided questions and answers.
Learning Objectives:
• Define Clinical Validation and summarize the process.
• Identify common scenarios a Clinical Validation Query may be needed & high-risk diagnoses.
• Explain who authors Clinical Validity Queries.
What is the e4health CDI Leadership Roundtable?
The goal for the virtual CDI Leadership Roundtable Discussion is for CDI leaders to explore specific topics within CDI, learn about the topic and from each other. During each roundtable, e4health CDI Leader’s will present a CDI topic, spend time sharing current industry standards or some education regarding this topic and then open with probing questions for group discussion.
Who should attend the e4health CDI Leadership Roundtable?
The focus of this group is for those who have influence over CDI program process, policy, and education.
Why should I attend the e4health CDI Roundtable?
This will be a wonderful place to learn, share your wins and challenges and collaborate with other CDI leaders across the industry. Also, after completing a survey, free ACDIS CEUs will be earned.
The information and opinions presented here are based on the experience, training, and interpretation of e4health. Although the information has been researched and reviewed for accuracy, e4health does not accept any responsibility or liability regarding errors, omissions, misuse, or misinterpretation. This information is intended as a guide; it should not be considered a legal/consulting opinion or advice.