Adult Obesity
Definition
Obesity: Recognized as a BMI > 30.
Morbid obesity: BMI > 40 or > 35 with at least one obesity related comorbid condition such as diabetes, heart disease, stroke, hypertension or arthritis.
Drug-induced obesity (iatrogenic obesity): Obesity as an adverse effect of prescribed medications such as corticosteroids, some diabetes medications, antidepressants, Depakote and heartburn drugs.
Morbid obesity with alveolar hypoventilation (OHS or Pickwickian syndrome): This condition is notable for an individual to have alveolar hypoventilation while awake that cannot be attributed to other causes.
Diagnostic Criteria
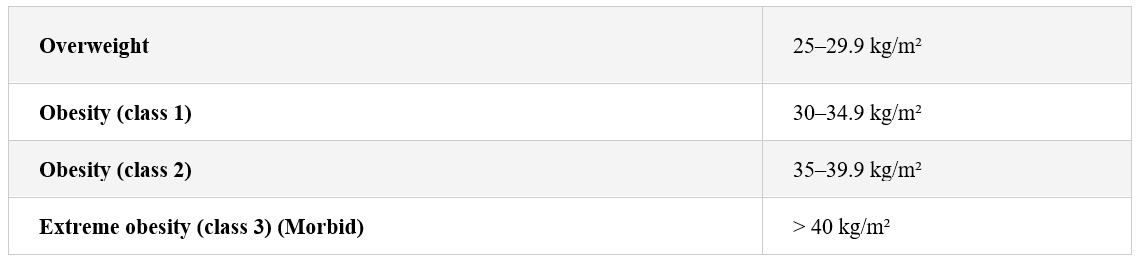
-
- All patients should have a height and weight measurement for each admission, or at least a reliable measurement.
- A BMI of 18.5-24.9 is considered normal per the Center for Disease Control (CDC).
Coding Considerations
- The E66 code grouping has a “use additional code” note indicating that the BMI should be coded as well.
- BMI can be coded based on documentation other than the patient’s provider. This information is typically documented by other clinicians involved in the care of the patient (e.g., a dietitian often documents the BMI). BMI codes should only be assigned when there is an associated, reportable diagnosis (such as obesity).
- E66.01 Morbid (severe) obesity due to excess calories
- Excludes 1 note
- E66.2 Morbid obesity with alveolar hypoventilation
- Excludes 1 note
- The obesity class should be documented in the medical record by the provider for these codes to be assigned. The obesity class codes can be reported with other obesity codes in the classification found in Chapters 4 and 15 to fully describe the condition. However, if both class 3 obesity and morbid obesity are documented, only a code for class 3 obesity should be assigned as it is more specific.
Review the following Coding Clinics:
-
- AHA Coding Clinic, Fourth Quarter 2024, p. 11
- AHA Coding Clinic, Third Quarter 2022, p. 6
- AHA Coding Clinic, Fourth Quarter 2018, p. 77
- AHA Coding Clinic, Fourth Quarter 2018, p. 77
- AHA Coding Clinic, Fourth Quarter 2018, p. 78
Fiscal year 2025 expanded code subcategory E66.8, Other obesity, to include the following codes:
-
- E66.811, Obesity, class 1
- E66.812, Obesity, class 2
- E66.813, Obesity, class 3
- E66.89, Other obesity not elsewhere classified
These codes do not provide a CC as a secondary diagnosis.
CDI Practice Considerations
- BMI codes may be based on medical record documentation provided by non-physician healthcare professionals.
- BMI should not be coded unless there is an associated, reportable diagnosis documented by the provider.
- When obesity is identified as drug-induced, additional codes must be assigned to capture both the adverse effect and the specific medication involved.
- Documentation of morbid obesity contributes to Hierarchical Condition Category (HCC) coding and risk adjustment. Obesity may also influence quality measure risk adjustment tools such as the Elixhauser Comorbidity Index, the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP), Patient Safety Indicators (PSIs) 11, 12, and 14, as well as publicly reported hospital ranking methodologies. Query as necessary when clinical indicators support a more specific diagnosis.
- Patients with substantial edema or ascites, many of whom are malnourished, may have a high BMI compared to their “dry weight” BMI.
- It is essential for providers to clearly document the relationship between a patient’s weight and their comorbid conditions. Doing so substantiates the diagnosis of morbid obesity and provides stronger justification for coding. This documentation also supports the clinical rationale for how morbid obesity impacts the management and treatment of other chronic conditions.
Looking for CDI help?
e4health CDI Education
Need help to earn CEUs or education your team? Visit the IQ Education Center and get your free account or contact us for more information. e4health is dedicated to elevating the business of healthcare. We are committed to offering support and the most current information and updates to collaborate with coding and CDI professionals to realize their fullest potential. We enthusiastically seek opportunities to develop ourselves and each other. We understand that knowledge is the key to success for our clients navigating the ever-changing health information management landscape.
Earn FREE ACDIS CEUs when you join Staci Josten, RN, BSN, CCDS, Alyson Swinehart, BSN, RN, CCDS, and other CDI leaders for a roundtable discussion regarding important, timely industry topics! The topic for November’s discussion is Mindset Matters: Inspiring CDI Growth Through Learning. We will provide background on this topic, share industry insights, and facilitate collaborative discussion with guided questions and answers.
Objectives:
- Understand the concept of growth mindset
- Identify how mindset impacts our CDI practice
- Learn strategies to overcome barriers to growth mindset
Click here to register!
What is the e4health CDI Leadership Roundtable?
The goal for the virtual CDI Leadership Roundtable Discussion is for CDI leaders to explore specific topics within CDI, learn about the topic and from each other. During each roundtable, e4health CDI Leader’s will present a CDI topic, spend time sharing current industry standards or some education regarding this topic and then open with probing questions for group discussion.
Who should attend the e4health CDI Leadership Roundtable?
The focus of this group is for those who have influence over CDI program process, policy, and education.
Why should I attend the e4health CDI Roundtable?
This will be a wonderful place to learn, share your wins and challenges and collaborate with other CDI leaders across the industry. Also, after completing a survey, free ACDIS CEUs will be earned.
The information and opinions presented here are based on the experience, training, and interpretation of e4health. Although the information has been researched and reviewed for accuracy, e4health does not accept any responsibility or liability regarding errors, omissions, misuse, or misinterpretation. This information is intended as a guide; it should not be considered a legal/consulting opinion or advice.
